While its origins are unknown and often shuttled between biological and psychological factors it is commonly found in families with psychotic disorders such as somatic delusions leading to a suspicion that both conditions are linked. Contingency management CM is the application of the three-term contingency or operant conditioning which uses stimulus control and consequences to change behavior.

Neurocognitive Disorders Case Study Abdullah Is A 72

Criteria For Psychosis In Major And Mild Neurocognitive Disorders International Psychogeriatric Association Ipa Consensus Clinical And Research Definition The American Journal Of Geriatric Psychiatry
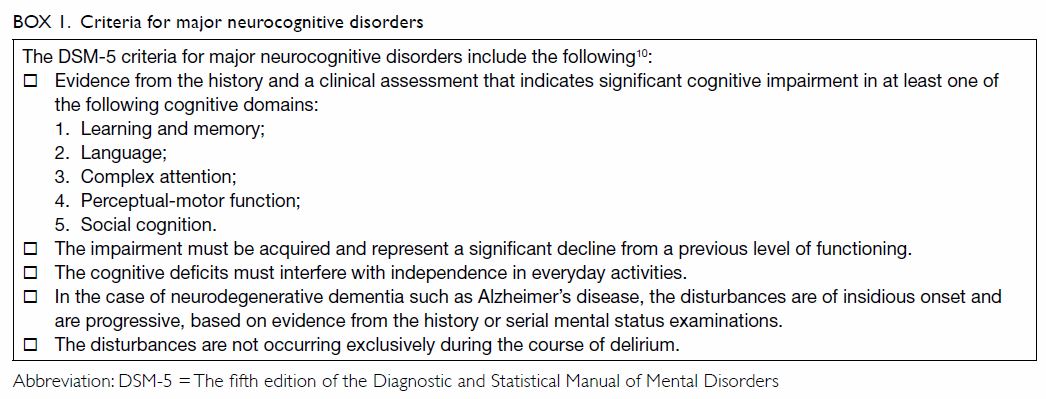
Assessment And Diagnosis Of Dementia A Review For Primary Healthcare Professionals Hkmj
The subgenual cingulate is a major target in the treatment of.

Major neurocognitive disorder treatment. However not all care professionals and organizations are likely to use the new term. However some treatments can alleviate symptoms or slow the progression of cognitive decline. Individuals with these disorders may show symptoms that point to delusional disorder eg simple persecutory delusions in major neurocognitive disorder would be diagnosed as major neurocognitive disorder with behavioral disturbance.
For alcohol or malnourished cases vitamin B supplements are recommended and for extreme cases life-support can be used. Adjustment disorder sometimes referred to as situational depression is a lengthy abnormal and excessively negative reaction to an identifiable life stressor. Probate Code 811 23565.
3 By 2020 MDD is estimated to become the second largest cause of disability. Before delirium treatment the cause must be established. Whether diagnosed as mild or major the mental and behavioral symptoms of the nine recognized neurocognitive disorders are similar according to the DSM-5 and typically include a.
Examples of disorders that we evaluate in this category include major neurocognitive disorder. In an open-label study of 24 patients with major depressive disorder. Erbes C Tye S et al.
The reaction is more severe than. The terms major neurocognitive disorder and minor neurocognitive disorder are likely to be used only by some health care professionals and organizations. CNS Vital Signs Testing.
Major neurocognitive disorder replaces the DSM-IVs term dementia or other debilitating conditions. The proposed conservatee HAS the capacity to give informed consent to the administration of medications appropriate to the care and treatment of major neurocognitive disorders including. In practice an individuals diagnosis could be Minor Neurocognitive Disorder AD subtype or Major Neurocognitive Disorder HIV-associated subtype.
Major or Mild Neurocognitive Disorder due to AD Alzheimers Disease also commonly referred to as Alzheimers Dementia is a DSM-5 Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders fifth edition diagnosis assigned to individuals who are experiencing cognitive deficits directly related to the onset and progression of Alzheimers Dementia. The DSM-5 distinguishes between mild and major neurocognitive disorders. An incapacitating episode is a period during which bed rest and treatment by.
A pivotal addition is mild neurocognitive disorder mNCD defined by a noticeable decrement in cognitive functioning that goes beyond normal changes seen in aging. Major neurocognitive disorder is not currently curable. Delirium major neurocognitive disorder psychotic disorder due to another medical condition and substancemedication-induced psychotic disorder.
In older adults the term Mild Cognitive Impairment MCI has been in use for the past decade describing a state intermediate in severity between normal aging and dementia mostly Alzheimers type and frequently a precursor to a. 1 2 The clinical characteristics of MDD include low self-esteem loss of interest in previously interesting activities and changes in appetite. MAJOR NEUROCOGNITIVE DISORDER ATTACHMENT TO CAPACITY DECLARATIONCONSERVATORSHIP.
A computerized neurocognitive testing platform that assesses how well your brain is managing tasks such as working memory verbal memory concentration processing speed and executive functioning. CM originally derived from the science of applied behavior analysis ABA but it is sometimes implemented from a cognitive-behavior therapy CBT framework as well such as in dialectical behavior therapy or DBT. Major depressive disorder MDD is a common psychiatric disorder in clinical practice which is associated with enormous public health costs and morbidity.
Currently the Alzheimers Association for example uses the word dementianot neurocognitive disorder. Paranoid Personality Disorder This condition is characterized by a strong distrust of people without any basis for suspicions. Medication such as antipsychotics or benzodiazepines can help reduce the symptoms for some cases.
Or substance-induced cognitive disorder associated with drugs. Mild Neurocognitive Disorder The diagnosis of mild neurocognitive disorder in the fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manu-al of Mental Disorders DSM-5 provides an opportunity for early detection and treatment of cognitive decline before patients deficits become more pronounced and progress to major neurocognitive disor-. Mental impairments resulting from medical conditions such as a metabolic disease for example juvenile Tay-Sachs disease human immunodeficiency virus infection vascular malformation progressive brain tumor or traumatic brain injury.
Mild and major neurocognitive disorder. Page 1 of 1. Neurocognitive performance of.
9326 Major or mild neurocognitive disorder due to another medical condition or substancemedication-induced major or mild neurocognitive disorder 9327 Removed 9400 Generalized anxiety disorder.

Chapter 14 Neurocognitive Disorders And Disorders Related To Aging Ppt Download
Introduction Interventions To Prevent Age Related Cognitive Decline Mild Cognitive Impairment And Clinical Alzheimer S Type Dementia Ncbi Bookshelf

Neurocognitive Disorders 1

Frontotemporal Neurocognitive Disorder
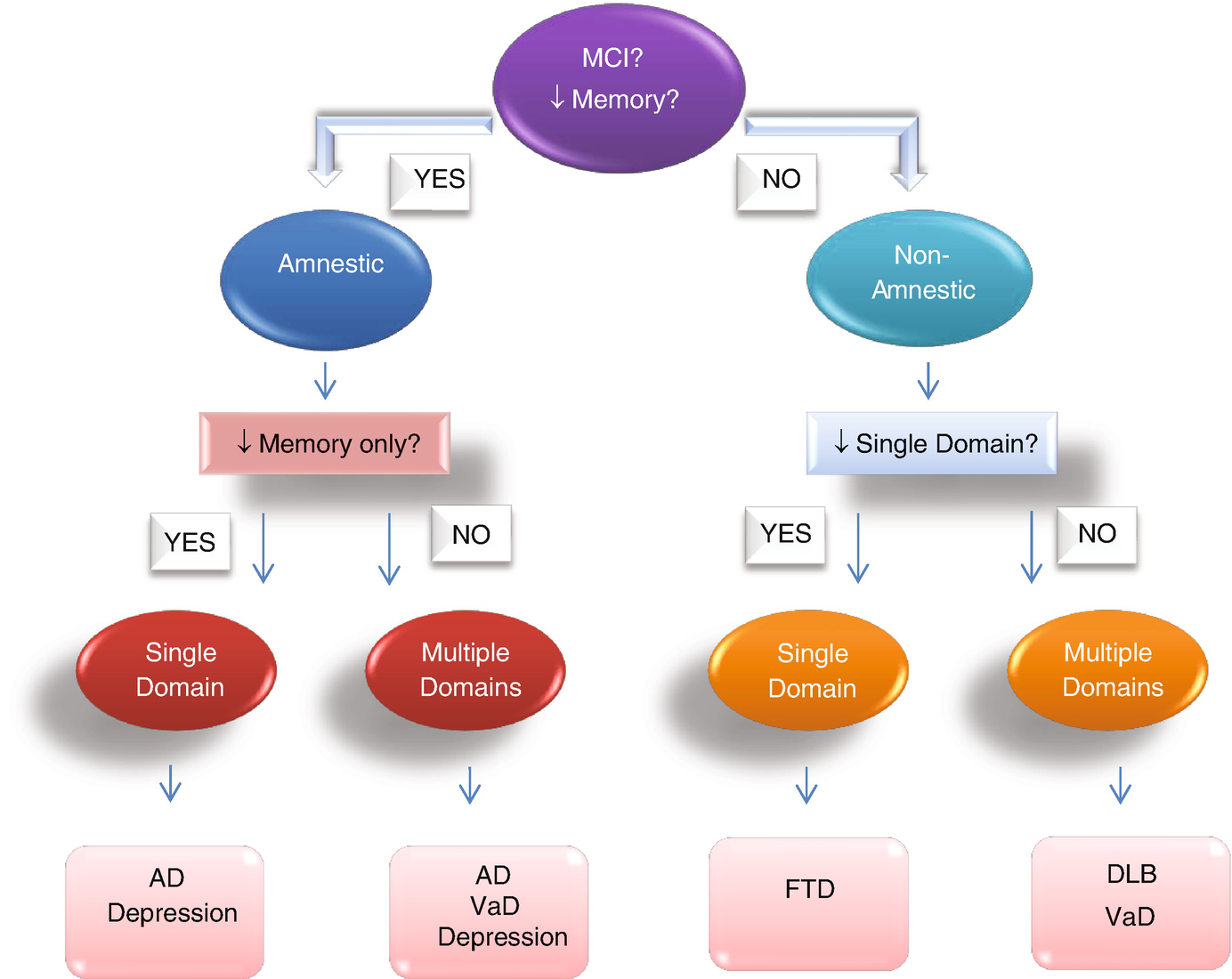
Common Major And Mild Neurocognitive Disorders Alzheimer Disease Frontotemporal Lewy Body And Vascular Types Springerlink

Treatment Approaches To Neurocognitive Disorders Psychiatric Annals

Major Neurocognitive Disorder With Behavioral Disturbance Behavioral And Psychological Symptoms Of Dementia Bpsd Springerlink
1
